In today’s digital age, information security is more important than ever. With cyber threats on the rise, it is crucial for everyday users to understand the basics of protecting their personal data. In this article, we will discuss key principles, strategies, and best practices to help you strengthen your online security. By the end of this post, you’ll have a better understanding of how to safeguard your digital assets and minimize your vulnerability to cyber threats.
There are some things that you can’t control. Breaches of other people’s systems, unknown vulnerabilities in software you use, the phase of the moon – yes they are important, but you can’t control them directly – so focus on what you can impact! And in my experience the phase of the moon directly correlates to some seriously bat-shit events 🤔.
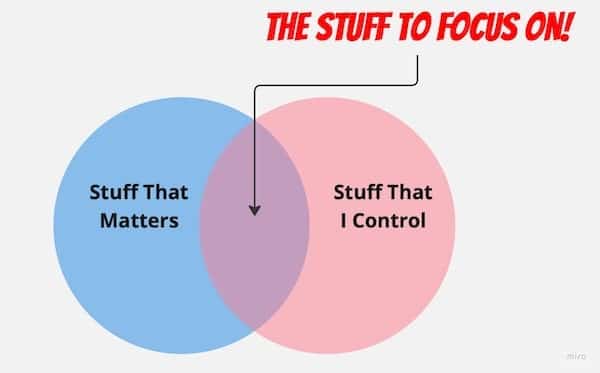
For the impatient – just skip to the recommendations …
Understanding Information Security
What is Information Security? Information security refers to the process of protecting digital data from unauthorized access, modification, disclosure, or destruction. This includes implementing measures to safeguard the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, whether it’s your personal data or that of your organization.
Key Principles of Information Security
Information Security Practitioners love to make things more complex than they really are and talk about the “CIA Triad” which is Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These are described below, but honestly don’t over think it … I’ll provide three pillars that I use after.
Confidentiality: Confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized individuals. Encrypting data, using strong passwords, and limiting access to sensitive information are some of the ways to maintain confidentiality.
Integrity: Integrity involves maintaining the accuracy and consistency of data throughout its lifecycle. This means ensuring that information is not altered or tampered with in any unauthorized way. Practices like version control, hashing, and digital signatures can help ensure data integrity.
Availability: Availability refers to the accessibility of information when it’s needed. To ensure availability, you should have reliable and resilient systems, as well as backup plans in place to minimize downtime and protect against data loss.
Wasn’t that fun and well … no it wasn’t. When thinking about security I tend to break things down into three pillars People, Processes, Technology.

People – We are all responsible for the security of our information, devices and well, everything we do (or don’t do). This is an often ignored subject, but you are here reading this, so you at least want to take this responsiblitity seriously – even if you are not yet sure how.
Processes – These do not necessarily mean step by step documents and annoying sing-offs etc. For a home user, just having a schedule to remind yourself to change passwords, backup data regularly and install patches to your computing devices … now in a corporate situation its a much different reality – but again — the venn diagram above … 😂
Technology – Ok, now this is what most people think about when talking “information security”. Technology is one of the three legs, but only as important as the other two. Some of the technologies you should think about are Virtual Private Networks, Anti-Virus/Anti-Malware, Personal Firewalls, Multi-Factor Authentication, and Password Managers.
This leads us to the next section – as we need to assume one or more of these controls will fail, and fail miserably!
The Importance of a Multi-Layered Security Approach
Defense in Depth, or belt and suspenders: A defense in depth strategy involves implementing multiple layers of security controls to protect your information. This approach ensures that even if one layer is compromised, other layers can still provide protection.
The Principle of Least Privilege: The principle of least privilege dictates that users should only have the minimum level of access necessary to perform their job functions. This reduces the potential for unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive information. For example, don’t overshare your personal information on social media as this is how social engineers target people in phishing campaigns, and can even guess your passwords or challenge response questions.
Best Practices for Everyday Users
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Create strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or common words. Consider using a password manager to help you generate and store complex passwords securely. I personally use 1Password, especially after a number of breaches at another solution. Never use the same password on different sites! This goes for your phone lock screen too!
- Encrypt Your Data: Turn on your operating systems’ Disk Encryption. For Windows, this is done in bitlocker, and for Macs in FileVault. For iOS devices turning the passcode on your iPhone/iPad automatically enables this. For Android devices, check out this article.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to provide additional verification, such as a fingerprint or a code sent to your phone. Enable 2FA on all accounts that offer this feature.
- Keep Your Software Up-to-Date: Regularly update your operating system, applications, and antivirus software to protect against new vulnerabilities and threats. Set up automatic updates whenever possible. Check out this guide on keeping your software up-to-date.
- Be Cautious with Public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi networks can be insecure and expose your data to potential attackers. Avoid connecting to public Wi-Fi when dealing with sensitive information, or use a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your connection. Private Internet Access is a cross platform tool that works on your Windows, Mac, or Linux computer as well as Apple or Android mobile devices. It is simple to set up and use – and it’s relatively cheap for the protections it gives.
- Beware of Phishing Scams: Cybercriminals often use phishing emails and websites to trick users into revealing their personal information. Be cautious when clicking on links in emails or entering your credentials on unfamiliar websites. Verify the authenticity of the sender and the website before providing any sensitive information.
- Regularly Back Up Your Data: Create regular backups of your important files and store them in multiple locations, such as an external hard drive and a secure cloud storage service. This way, you can easily recover your data in case of a cyber attack or hardware failure. Learn more about backing up your data.
- Secure Your Home Network: Implement security measures for your home network, such as changing default router settings, enabling a firewall, and securing your Wi-Fi network with a strong password and encryption. For more tips, check out this guide on securing your home network.
- Educate Yourself on Social Engineering Tactics: Social engineering is the manipulation of individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. Familiarize yourself with common social engineering tactics and learn how to recognize and avoid them.
- Monitor Your Online Accounts and Credit Reports: Regularly review your online accounts for any unauthorized activity and check your credit reports to detect signs of identity theft. In the US, you are entitled to one free credit report per year from each of the three major credit reporting agencies.
- Dispose of Digital Devices Securely: When disposing of digital devices, ensure that all personal data is securely erased. This may involve using a data wiping tool or physically destroying the storage medium. Learn more about disposing of digital devices securely.
Wrapping it all up: Understanding and implementing information security best practices is crucial for protecting your personal data in today’s digital world. By following the guidelines outlined in this post, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cyber threats and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your digital assets. Stay informed and vigilant to maintain a strong security posture in an ever-evolving cyber landscape.




